Browse the full results of the Arab University Rankings 2023
The top-scoring country in the Middle East, the United Arab Emirates (UAE), also has a fairly equal performance in its collaborations with countries both outside the Arab region and within.
With an overall score of 79.5, the UAE leads the region among countries with five or more ranked institutions. Khalifa University and the University of Sharjah are the nation’s highest scorers.
Arab University Rankings 2023: results announced
Lebanon, which is northwest of the Gulf, is the second best, with an average overall score of 79. Its top-performing institutions are Beirut Arab University and American University of Beirut. Saudi Arabia places third with an average score of 65.1 across its universities.
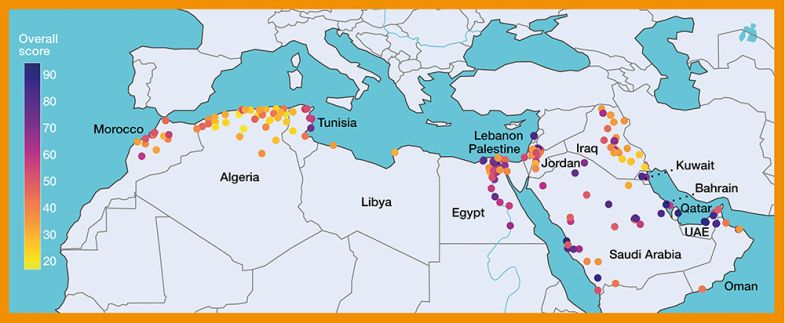
Map showing location and overall score of universities in the Arab university rankings 2023
The first graph displays the regional spread of institutions, colour-coded for overall score, and the concentration of strong violet dots in the Gulf region visualises this hub for high scorers.
The second graph charts the relationship between international co-authorship and regional Arab collaborations.
International collaboration versus Arab collaboration
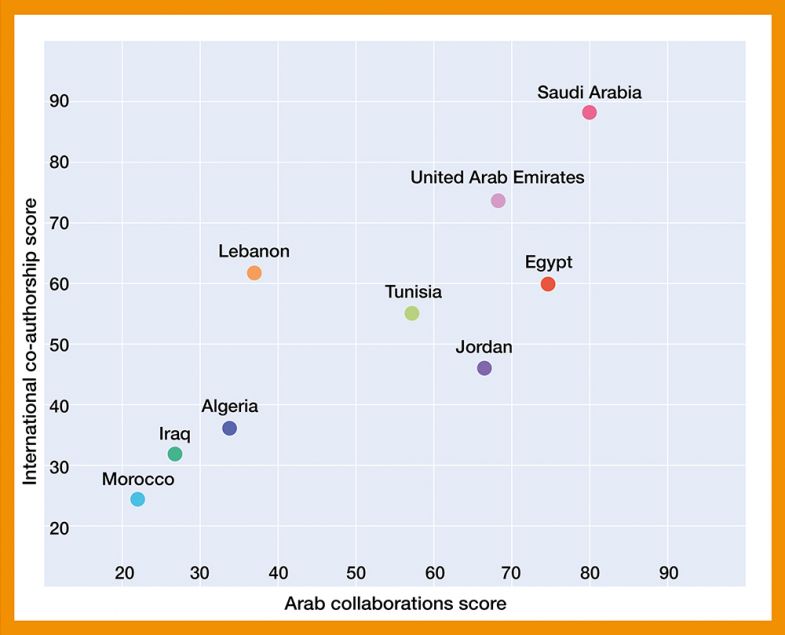
Countries including the UAE and Saudi Arabia, along with Morocco, Iraq, Algeria and Tunisia, lie on the slant of the graph, signalling a fairly equal performance in their collaborations near and far.
Algeria, for example, has a low overall score, but a more level performance when comparing its work with Arab institutions with those further afield. This is seen in its international co-authorship score of 36.1, which does not diverge much from its 33.8 mark for Arab collaborations.
Towards the top end of the slant are Saudi Arabia and the UAE, which show high scores and similarly strong outputs across both types of collaboration.
Meanwhile, other nations, such as Jordan and Egypt, fall outside the diagonal, faring better in their collaborations with universities in the Arab region. Egypt scores 74.7 for Arab collaborations, which is significantly higher than its 59.9 for international co-authorship.
Lebanon swings the other way, with a strength in international co-authorships. This is clear with the 61.7 score versus 37 for Arab collaborations.